Download And Install R Packages
Installing R Packages
Jeffrey Leek
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
R Packages
-
When you download R from the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN), you get that ``base" R system
-
The base R system comes with basic functionality; implements the R language
-
One reason R is so useful is the large collection of packages that extend the basic functionality of R
-
R packages are developed and published by the larger R community
Obtaining R Packages
-
The primary location for obtaining R packages is CRAN
-
For biological applications, many packages are available from the Bioconductor Project
-
You can obtain information about the available packages on CRAN with the
available.packages()function
a <- available.packages() head(rownames(a), 3) ## Show the names of the first few packages ## [1] "A3" "abc" "abcdeFBA" -
There are approximately 5200 packages on CRAN covering a wide range of topics
-
A list of some topics is available through the Task Views link, which groups together many R packages related to a given topic
Installing an R Package
-
Packages can be installed with the
install.packages()function in R -
To install a single package, pass the name of the lecture to the
install.packages()function as the first argument -
The following the code installs the slidify package from CRAN
install.packages("slidify") -
This command downloads the slidify package from CRAN and installs it on your computer
-
Any packages on which this package depends will also be downloaded and installed
Installing an R Package
-
You can install multiple R packages at once with a single call to
install.packages() -
Place the names of the R packages in a character vector
install.packages(c("slidify", "ggplot2", "devtools")) Installing an R Package in RStudio
Installing an R Package in RStudio
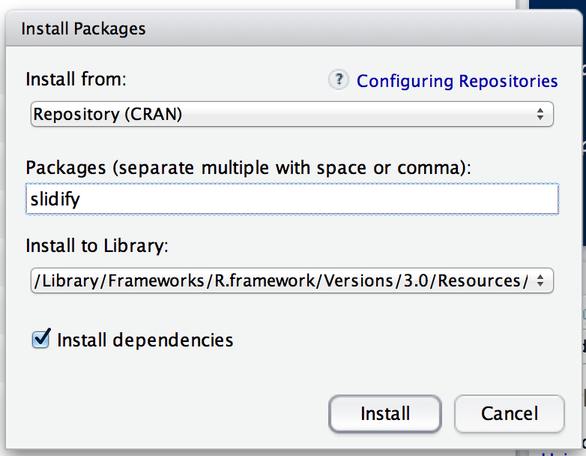
Installing an R Package from Bioconductor
- To get the basic installer and basic set of R packages (warning, will install multiple packages)
source("http://bioconductor.org/biocLite.R") biocLite() - Place the names of the R packages in a character vector
biocLite(c("GenomicFeatures", "AnnotationDbi")) http://www.bioconductor.org/install/
Loading R Packages
-
Installing a package does not make it immediately available to you in R; you must load the package
-
The
library()function is used to load packages into R -
The following code is used to load the ggplot2 package into R
library(ggplot2) -
Any packages that need to be loaded as dependencies will be loaded first, before the named package is loaded
-
NOTE: Do not put the package name in quotes!
-
Some packages produce messages when they are loaded (but some don't)
Loading R Packages
After loading a package, the functions exported by that package will be attached to the top of the search() list (after the workspace)
library(ggplot2) search() ## [1] ".GlobalEnv" "package:kernlab" "package:caret" ## [4] "package:lattice" "package:ggplot2" "package:makeslides" ## [7] "package:knitr" "package:slidify" "tools:rstudio" ## [10] "package:stats" "package:graphics" "package:grDevices" ## [13] "package:utils" "package:datasets" "package:methods" ## [16] "Autoloads" "package:base" Summary
-
R packages provide a powerful mechanism for extending the functionality of R
-
R packages can be obtained from CRAN or other repositories
-
The
install.packages()can be used to install packages at the R console -
The
library()function loads packages that have been installed so that you may access the functionality in the package
Source: https://jtleek.com/modules/01_DataScientistToolbox/02_09_installingRPackages/
Posted by: brightcolours03.blogspot.com